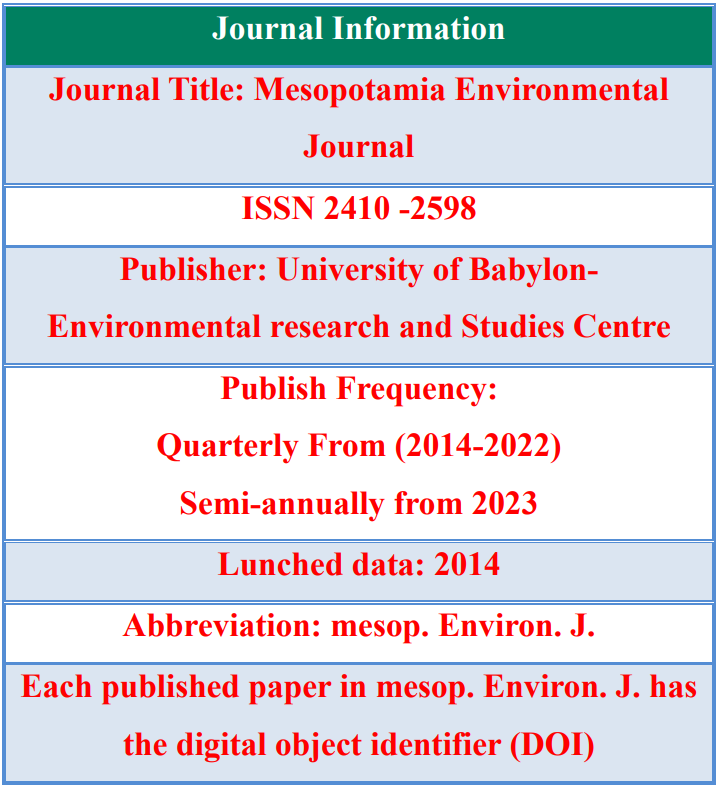
Measurement of natural radioactivity levels in the soils of some universities campus of babylon
Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the level of radioactivity in the surface soils of Babylon University, Islamic University, Al-Mustaqbal University respectively by measuring the activity concentrations of various radiation emissions. It was measured 50 random deferent sites within Babylon University, and 22 random sites within Islamic University, as well as, 10 sites within Al- Mustaqbal University respectively by distance 30 cm from the surface soil involved all the departments, colleges and infrastructures. The results showed that the measurements were generally close together. For Babylon university, the highest value registered at the location (31) and the lowest value registered at two location: (9),(21). While for the Islamic University, the highest value registered at the location (12), (20) and the lowest value registered at two location: (1),(2).where for Al- Mustaqbal University, the highest value registered at the location (6) and the lowest value registered at location (7). It was noted that the study area is free from radioactive hazards, so the study area is save for human health.